Definition: Product managers drive product vision, strategy, and execution across cross-functional teams.
Roles: Specialized roles include growth, technical, and data product managers with unique focuses.
Responsibilities: PMs lead research, roadmap creation, testing, and performance analysis of products.
Skills: Successful PMs are organized, empathetic, strategic, and strong decision-making leaders.
What Is Product Management?
Product management is a role within a product development team focused on guiding products through their lifecycle—from ideation to launch and ongoing improvement—to ensure they successfully meet user needs and achieve business objectives.
Although relatively new in digital companies, product management has grown significantly alongside Agile methods. Product managers define a product’s vision, prioritize features, and collaborate with design, engineering, and business teams.
Why Is Product Management Important?
Like executive chefs who guide quality without owning the restaurant, product managers shape product vision and experiences without owning the business.
They bridge UX, engineering, and business goals, aligning stakeholders around a unified product strategy.
Unlike project management—which focuses on tasks and resources—product management emphasizes strategic vision and customer value.
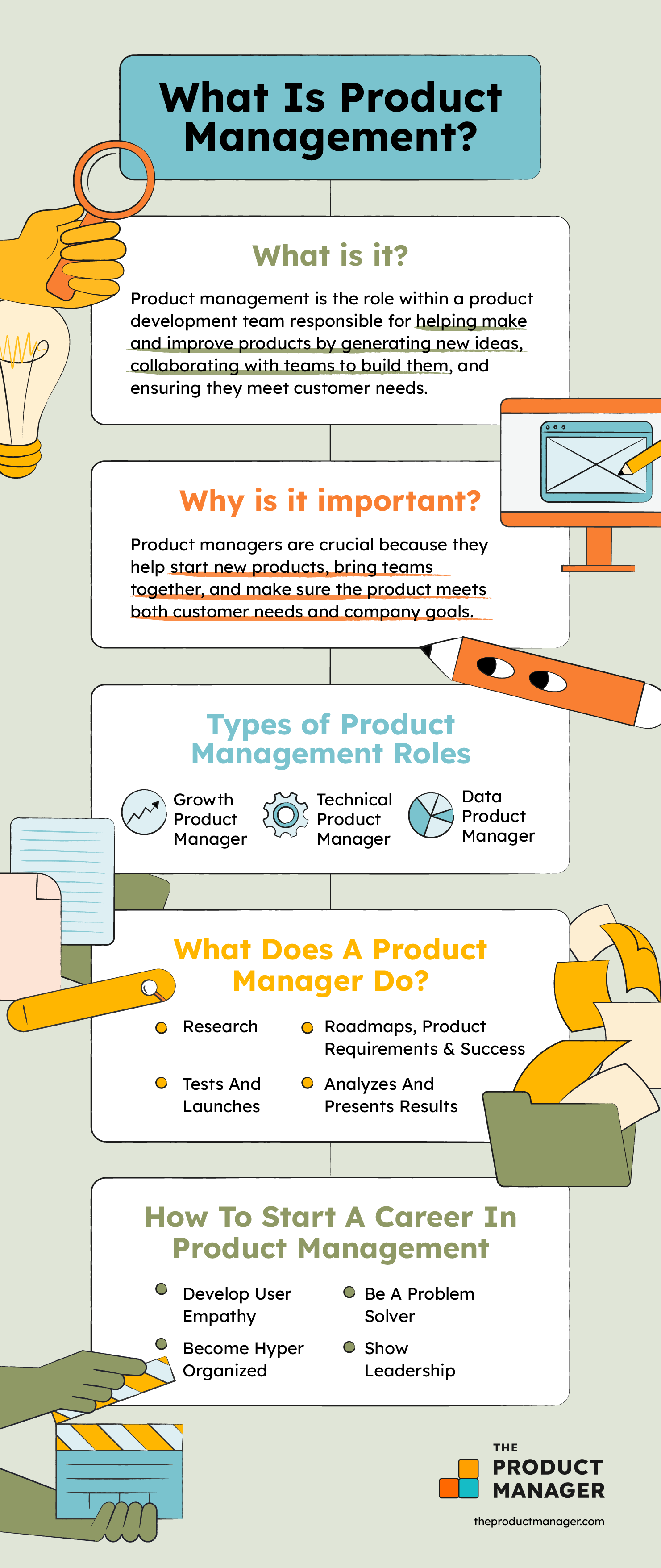
Types Of Product Management Roles
While the core functions of a PM are essentially the same across all types of product management roles and product teams, there are some nuances that align with different titles and role descriptions.
You will encounter titles that define different levels of experience in product management, such as chief product officer, product owner, and associate product manager.
..What makes a growth-minded PM is they actually look at their area of business as if they’re like a mini CEO of their product area.
Some common types of specialized product management roles you’ll see are:

Growth Product Manager
A growth product manager is primarily focused on furthering a specific metric their company has set to measure the growth of their business. Typically, growth PMs work closely with product marketing and traditional marketing teams in order to ensure their initiatives are expanding their product reach.
Most growth product managers run frequent short-term experiments to measure the success of their new feature or project, and pivot to new initiatives quickly in order to meet the demands of the business. Everything from copy to pricing is on the table for testing, and they may help in defining go-to-market strategies.
Growth product managers would benefit from experience or education in digital marketing, psychology, or advertising.
Technical Product Manager
A background in engineering or development is almost always required for technical product management roles, as this type of PM works hand in hand with engineering teams to improve things like a product’s core functionality or a company’s tech stack, security, or other parts of their digital infrastructure. This is often done with the help of product development software.
These PMs are less focused on the appearance of a product and instead are dedicated to ensuring that its inner workings are solid.
Often, technical product managers are career changers who started out as engineers.
Data Product Manager
If you love working with numbers or were a math wiz in school, then a data product management role could be a great fit. Working with business analytics teams and data scientists, data PMs create use cases that organizations use to measure success for their new product and feature releases.
Often they are responsible for ensuring that customer interactions are tracked properly across the product interface, so that other PMs or stakeholders can gain valuable insights into how users are navigating the product.
A degree in mathematics, finance, or data science would be a great help to any aspiring data PM.
What Does A Product Manager Do?
So, is a career in product management right for you?
A product manager's first few months and subsequent day-to-day responsibilities vary across different types of businesses. However, all product management roles entail certain universal tasks that are critical to furthering a product development lifecycle.
Research
A primary focus of a PM is the end-user of their product. Therefore, much of a product manager’s time is spent conducting and analyzing both market research and user research, either in partnership with dedicated research teams or on their own, depending on the size of their organization.
PMs must analyze customer needs and product-market fit, and advocate for these data points to be part of the company’s prioritization discussions. Gathering customer feedback is critical to the success of a new product.
Defines Roadmap, Product Requirements, And Success
After conducting research, PMs help defines the organization’s product roadmap, an essential product planning tool that essentially documents the workflow for when and how each feature or product will be released.
Working with product management teams and scrum masters, each new product build will be broken up into various incremental steps that will be executed over a set period of time-based on available resourcing and are typically broken up by a quarter.
PMs are responsible for forecasting delivery timelines, ensuring that the engineering team and UX designers they work with manage a backlog of ideas, are prioritizing the right things, and are aware of all of the requirements and steps needed to complete the product’s vision.
Tests And Launches
Once the development process is complete, PMs lead the testing of the new feature and often do so through setting up experiments and iterations. Sometimes large initiatives are broken up into smaller phases, such as a “beta” launch. PMs are responsible for measuring the success of each phase, and working with engineering to address any issues that arise during testing.
Analyzes And Presents Results
When a new feature is live and in front of real customers or users, the product manager is typically responsible for communicating the successes or shortfalls of the product to business leadership. They leverage several different analytics tools and reports to ensure that the product is meeting the expectations set at the research phase.
-

LaunchNotes
Visit WebsiteThis is an aggregated rating for this tool including ratings from Crozdesk users and ratings from other sites.4.9 -

monday dev
Visit WebsiteThis is an aggregated rating for this tool including ratings from Crozdesk users and ratings from other sites.4.6 -

ClickUp
Visit WebsiteThis is an aggregated rating for this tool including ratings from Crozdesk users and ratings from other sites.4.7
How To Start A Career In Product Management
Product management is a career that fits many types of backgrounds and skill sets. There is no linear path to get into a PM role, and it is a great option for those who are interested in technology but are not sure how to apply their past experience to a role in tech. Here are just some of the product management skills and tips that can help you get into a PM role:
Develop User Empathy
The most important skill to have as a PM is empathy for your user. Start to pay attention to the things that both delight and bother you about products that you use in your everyday life. What are your pain points when using the product, and how would make the customer experience better? This mindset is critical to your success as a product manager.
Be A Problem Solver
Great product managers are, at their core, problem solvers, both for their users and their organization. Be sure to illustrate how you have helped solve difficult problems in past roles and experiences, why these were important problems to solve, and how those solutions contributed to your org’s business goals.
Become Hyper Organized
Because the demands of each day as a PM can vary, they must be extremely organized. Start developing this habit early, and develop a prioritization system for things that you need to get done. Understand why you think something is more important than something else, and stick to it. A good sense of prioritization can make or break a successful product launch.
Show Leadership
Leadership is an important quality in a product manager, as you will be responsible for owning a product vision and collaborating with a team to get things done. To build this skill, you can volunteer at a startup and apply for internships, and, most importantly, don’t be afraid to challenge yourself. PMs need to be effective at decision-making, especially in high-pressure situations.
Demonstrate Your Interest
It can be helpful to demonstrate your interest in product management roles by subscribing to newsletters, watching videos, or reading material on the topic. If you're not sure where to start, we've put together a handy roundup of resources for product managers that includes a little something for every learning style.
There are also several certificates and on-demand courses you can take that can help you level up your skills and decide if a career as a PM is right for you. These courses are a great way to brush up on typical product terminology, such as "Agile" or "Scrum."
Conclusion
Product managers live at the intersection of technology and business leaders and play a critical role in ensuring that new features are a success for both their organization and their customers. For those with a passion for teamwork, strategic thinking, and creating awesome experiences for people, product management could be an extremely rewarding career choice.
Want to become a product manager? Subscribe to our newsletter and gain helpful insights into building your career as a PM.
Not sure where your PM career is headed? Stay ahead and check this podcast out: Future Trends In Product (with CK Hicks and Scotty Moon from Crema)
Worth Checking Out: How To Use monday.com For Product Management








